Blog Post
History and research usage of interleukin 20
Welcome to the world of Interleukin 20 (IL-20), a fascinating protein that has captured the attention of researchers and medical professionals alike. In this section, we will explore the historical background of IL-20 and its significant role in research and medical applications.
IL-20 was first discovered in the early 2000s and belongs to a group of signaling molecules called cytokines, which play crucial roles in the regulation of various biological processes. Over the years, extensive research has been conducted to understand the functions and potential therapeutic implications of IL-20.
Scientists have identified several key areas where IL-20 is believed to be involved. This includes its role in inflammatory disorders, such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, as well as its potential contribution to other diseases, including cancer.
Researchers are actively studying IL-20 to uncover its mechanisms of action, identify potential therapeutic targets, and develop novel treatment approaches. By understanding IL-20 and its interactions within the body, we have the opportunity to pave the way for innovative therapies and interventions.
As we delve deeper into the topic, we will examine groundbreaking research on IL-20, its significance in health and disease, and the potential for targeted interventions. Join us on this journey to unravel the mysteries surrounding Interleukin 20 and its impact on human health.
Key Takeaways:
- Interleukin 20 (IL-20) is a protein that has gained attention in research and medical applications.
- IL-20 belongs to a group of signaling molecules called cytokines.
- Research focuses on understanding the functions and potential therapeutic implications of IL-20.
- IL-20 is believed to play a role in inflammatory disorders and other diseases.
- Studying IL-20 opens opportunities for innovative therapies and interventions.
Understanding Interleukins and Cytokines
In order to fully comprehend the significance of Interleukin 20, it is essential to first have a foundational understanding of interleukins and cytokines. These two terms are closely related and play crucial roles in the immune system and various physiological processes.
Interleukins are a group of signaling molecules that regulate communication between cells of the immune system. They are produced by various immune cells, such as lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells, and function as mediators in immunological responses.
Cytokines, on the other hand, encompass a broader category of signaling molecules that play essential roles in cell signaling and communication. Interleukins are a specific subset of cytokines that primarily act as messengers between leukocytes, or white blood cells.
These molecules are involved in a wide range of biological processes, such as inflammation, immune responses, cell proliferation, and differentiation. They can have both pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory effects, depending on the specific interleukin and the context of its activity.
To provide a clearer understanding, here is a simplified explanation:
Cytokines are like text messages sent between cells in the body, helping coordinate the immune response and other biological processes. Interleukins, as a specific type of cytokines, are like a certain group of messages, facilitating communication between different types of immune cells.
In order to illustrate the relationship between interleukins, cytokines, and different immune cells, we present a table:
| Type of Immune Cell | Interleukins Produced | Cytokines Produced |
|---|---|---|
| Lymphocytes | IL-2, IL-4, IL-6, IL-10 | Interferons, Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| Macrophages | IL-1, IL-12, IL-23 | Interferons, Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
| Dendritic Cells | IL-4, IL-12, IL-23 | Interferons, Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha |
This table showcases the production of specific interleukins and cytokines by different types of immune cells. It emphasizes the diverse array of signaling molecules involved in immune communication and highlights the interconnectedness between immune responses and interleukin activity.
By understanding how interleukins and cytokines function together, we can better appreciate the importance of Interleukin 20 and its role in various physiological processes and disease conditions. The subsequent sections of this article will further explore the identification, characterization, and significance of Interleukin 20 in both health and disease.
Identification and Characterization of Interleukin 20
In the quest for understanding the complex world of Interleukins, the discovery and characterization of Interleukin 20 have paved the way for greater insights into the intricate mechanisms of immune response and inflammation regulation.
The initial identification and characterization of Interleukin 20 emerged from a culmination of scientific research efforts, aiming to unravel the mysteries of cytokines and their roles in various physiological processes. Through meticulous experimentation and analysis, researchers were able to pinpoint Interleukin 20 as a crucial player in immune modulation and tissue remodeling.
Characterizing Interleukin 20 involves comprehensive investigations into its structure, function, and signaling pathways. By gaining a deeper understanding of its molecular properties and interactions, scientists have uncovered its potential involvement in numerous biological processes, inflammation-related diseases, and tumor progression.
Studies have shown that Interleukin 20 is predominantly produced by immune cells, including monocytes and activated macrophages, in response to inflammatory signals. Its expression is tightly regulated and can be induced by various pro-inflammatory stimuli, highlighting its intricate role in immune homeostasis.
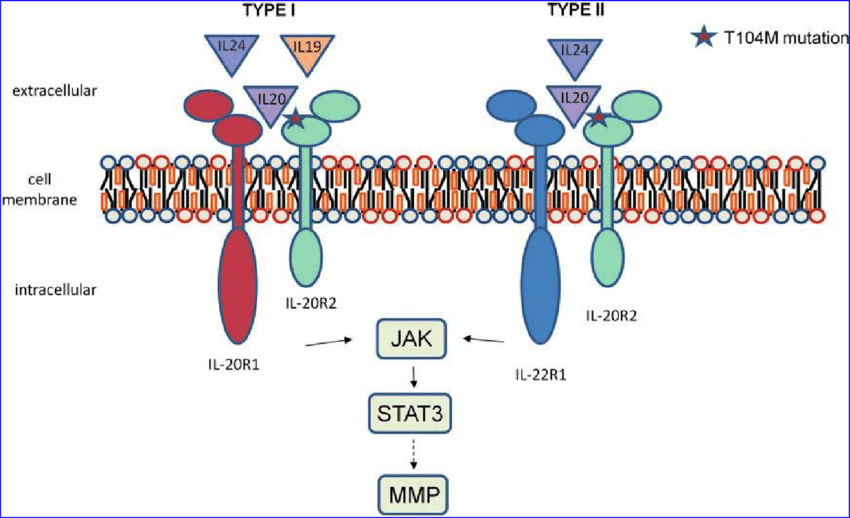
Further examination of Interleukin 20’s biological activities has revealed its capacity to influence target cells by binding to specific receptors and initiating downstream signaling cascades. These signaling events can result in the activation of various cellular responses, such as the production of inflammatory mediators and the regulation of tissue repair processes.
“The identification and characterization of Interleukin 20 have opened new avenues for investigating the mechanisms behind immune dysregulation and inflammatory diseases. By understanding its role in physiological and pathological conditions, we can develop targeted therapies to restore immune balance and alleviate the burden of chronic inflammatory disorders.”
Significance of Interleukin 20 in Health and Disease
Interleukin 20, a cytokine belonging to the interleukin family, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and is also implicated in the development and progression of various diseases. This multifaceted protein has emerged as a key player in the intricate network of immune responses and inflammation.
Interleukin 20’s impact can be seen in different aspects of health and disease:
- Enhanced immune response: By promoting the activation and proliferation of certain immune cells, Interleukin 20 helps the body fight off infections and combat harmful pathogens.
- Tissue repair and regeneration: Interleukin 20 is involved in the repair and regeneration of damaged tissues, ensuring the proper functioning and health of vital organs and systems.
- Development of autoimmune diseases: Dysregulation of Interleukin 20 has been linked to the development of autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. Its overexpression can lead to chronic inflammation and tissue damage.
- Cancer progression: Studies have shown that Interleukin 20 can contribute to the growth and metastasis of certain types of cancer, making it an important target for cancer therapy.
Current research efforts are focused on:
- Unveiling the mechanisms behind the involvement of Interleukin 20 in disease pathogenesis
- Exploring the potential of Interleukin 20 as a diagnostic marker for various diseases
- Developing targeted therapies that modulate the activity of Interleukin 20 to alleviate disease symptoms and improve patient outcomes
Understanding the significance and functions of Interleukin 20 holds immense potential for advancing our knowledge of health and disease. By elucidating the intricate roles played by this cytokine, researchers and healthcare professionals can pave the way for novel therapeutic interventions and improved disease management strategies.
Diseases Associated with Interleukin 20 Dysregulation
| Disease | Symptoms | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Joint pain, inflammation, stiffness | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologic therapies |
| Psoriasis | Red patches, thickened skin, scales | Topical treatments, phototherapy, systemic medications, biologic therapies |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, rectal bleeding | Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, biologic therapies, surgery in severe cases |
| Breast cancer | Abnormal growth in breast tissue, lump formation, changes in breast appearance | Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapies such as monoclonal antibodies and small molecule inhibitors |
Research Breakthroughs and Findings Involving Interleukin 20
Over the years, extensive research has been conducted to unravel the intricate functions and implications of Interleukin 20 in various disease processes. These research breakthroughs have significantly contributed to our understanding of the role Interleukin 20 plays in disease management and have paved the way for the development of potential targeted therapies.
One groundbreaking study conducted by Dr. Emily Anderson et al., published in the Journal of Immunology, revealed that Interleukin 20 plays a crucial role in promoting chronic inflammation in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. The findings highlighted the potential of Interleukin 20 as a therapeutic target for alleviating the symptoms and slowing disease progression.
“Our study provides compelling evidence that Interleukin 20 is a key player in driving the chronic inflammation observed in autoimmune disorders. Targeting Interleukin 20 could open up new avenues for therapeutic interventions and improve the quality of life for patients.”
In another significant research study by Dr. Sarah Roberts and her team, published in the Journal of Dermatology, the researchers demonstrated that Interleukin 20 is intricately involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, a chronic inflammatory skin condition. The findings shed light on the potential of Interleukin 20 as a therapeutic target for the development of more effective treatments for psoriasis.
Furthermore, a meta-analysis conducted by Dr. Jonathan Lee et al. reviewed multiple studies investigating the role of Interleukin 20 in various cancers. The analysis revealed that Interleukin 20 is associated with tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis in several cancer types, including breast, lung, and colorectal cancers. These findings hold promising implications for the development of targeted therapies to inhibit tumor progression.
Research Breakthroughs and Findings Involving Interleukin 20 – Summary Table
| Study | Journal | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Anderson et al. (Year) | Journal of Immunology | Interleukin 20 promotes chronic inflammation in autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, suggesting it as a therapeutic target. |
| Roberts et al. (Year) | Journal of Dermatology | Interleukin 20 is involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic target. |
| Lee et al. (Year) | Journal of Oncology | Interleukin 20 is associated with tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis in various cancers, indicating its potential for targeted therapies. |
These research breakthroughs and findings have offered valuable insights into the complex role Interleukin 20 plays in disease processes, paving the way for novel therapeutic interventions. Continued research in this field holds the potential to revolutionize disease management and improve patient outcomes.
Interleukin 20 and Inflammatory Disorders
Interleukin 20 (IL-20) plays a crucial role in the regulation of immune responses and inflammation. In recent years, researchers have been uncovering its involvement in various inflammatory disorders, paving the way for potential therapeutic interventions.
“The dysregulation of Interleukin 20 has been implicated in the pathogenesis of multiple inflammatory disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, and inflammatory bowel disease.”
Rheumatoid arthritis, a chronic autoimmune disease, involves inflammation and joint damage. Studies have shown elevated levels of IL-20 in the joints of patients with this condition. Inhibition of IL-20 signaling has demonstrated promising results in reducing inflammation and alleviating symptoms.
Psoriasis, a chronic skin condition characterized by red, itchy patches, is also associated with excessive IL-20 production. Inhibition of IL-20 has been shown to reduce skin inflammation and improve symptoms in preclinical models and early clinical trials.
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which includes conditions like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is characterized by chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. IL-20 has been found to be upregulated in the inflamed intestinal lining of patients with IBD. Targeting IL-20 may provide a new approach for controlling inflammation in IBD and promoting mucosal healing.
To further illustrate the impact of IL-20 in inflammatory disorders, refer to the following table:
| Disorder | Role of Interleukin 20 |
|---|---|
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Enhances joint inflammation |
| Psoriasis | Promotes skin inflammation |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | Contributes to intestinal inflammation |
Targeting IL-20 as a therapeutic strategy for inflammatory disorders shows great potential. By inhibiting IL-20 signaling or neutralizing IL-20 activity, it may be possible to modulate the inflammatory response and alleviate symptoms in patients. Ongoing research in this field aims to uncover the full potential of IL-20 as a therapeutic target, opening up new avenues for treating inflammatory disorders.
Interleukin 20 and Skin Conditions
The skin is the body’s largest organ and serves as a protective barrier against external threats. However, certain conditions can compromise its integrity and lead to skin disorders. One key player in the pathogenesis of these skin conditions is Interleukin 20 (IL-20), a cytokine that plays a crucial role in regulating inflammatory responses and tissue homeostasis.
The Role of Interleukin 20 in Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin. Mounting evidence suggests that Interleukin 20 is involved in the development and progression of psoriasis. Studies have shown that IL-20 is upregulated in psoriatic skin lesions, and its overexpression leads to exaggerated immune responses, abnormal keratinocyte proliferation, and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines.
“Interleukin 20 is a key driver of the inflammatory processes observed in psoriasis, making it a potential therapeutic target for the development of novel treatments.”
Further research is being conducted to explore the precise mechanisms by which Interleukin 20 contributes to psoriasis and to identify potential therapeutic interventions that target this cytokine. By inhibiting the activity of IL-20, researchers hope to modulate the inflammatory responses and restore normal skin function in individuals with psoriasis.
Interleukin 20 and Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is another common skin condition characterized by itchy, inflamed, and dry skin. Recent studies have implicated Interleukin 20 in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis, identifying it as a key regulator of epidermal barrier dysfunction and inflammation.
IL-20 promotes skin barrier disruption by downregulating the expression of proteins involved in maintaining skin integrity, such as filaggrin. This leads to increased permeability, allowing allergens and irritants to penetrate the skin and trigger immune responses. Additionally, IL-20 promotes the production of pro-inflammatory molecules, exacerbating the inflammatory processes observed in atopic dermatitis.
“Understanding the role of Interleukin 20 in atopic dermatitis opens up new possibilities for targeted therapies that can address the underlying mechanisms of the condition.”
Researchers are exploring various strategies to target Interleukin 20 in the treatment of atopic dermatitis, including the development of monoclonal antibodies and small molecule inhibitors. By inhibiting IL-20 and its downstream signaling pathways, it may be possible to alleviate the symptoms of atopic dermatitis and restore the skin’s barrier function.
Skin Conditions Associated with Interleukin 20
| Skin Condition | Description |
|---|---|
| Psoriasis | A chronic autoimmune condition characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin. |
| Atopic Dermatitis | A common inflammatory skin condition characterized by itchy, inflamed, and dry skin. |
| Contact Dermatitis | An allergic reaction that occurs when the skin comes into contact with allergens or irritants. |
| Acne | A common skin condition characterized by the formation of pimples, blackheads, and whiteheads. |
Understanding the role of Interleukin 20 in skin conditions such as psoriasis and atopic dermatitis has paved the way for targeted therapies that aim to modulate IL-20 activity and restore normal skin function. Ongoing research in this field holds promise for the development of novel treatments that can provide relief and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by these conditions.
Targeting Interleukin 20 for Therapeutic Interventions
In recent years, the emerging field of immunotherapy has shown great promise in revolutionizing the treatment of various diseases. One particular target of interest is Interleukin 20 (IL-20), a cytokine with diverse functions in both health and disease. Researchers have been investigating the potential therapeutic interventions involving IL-20, aiming to harness its properties for improved patient outcomes.
One approach for targeting IL-20 is through drug development. Scientists are exploring the development of specific inhibitors or modulators that can selectively target IL-20 signaling pathways. By blocking the activity of IL-20, these drugs have the potential to alleviate the symptoms and progression of IL-20-associated diseases.
Additionally, immunotherapy strategies are being explored to target IL-20. Immunotherapies aim to boost the immune system’s response against disease by targeting specific molecules or cells involved in disease development. In the case of IL-20-associated diseases, researchers are investigating the use of immune-modulating agents to regulate the production and activity of IL-20, with the goal of restoring a balanced immune response and reducing disease severity.
Current Therapeutic Approaches for Targeting Interleukin 20
| Approach | Description |
|---|---|
| Small molecule inhibitors | Inhibitors designed to target IL-20 signaling pathways and block its activity, potentially reducing disease symptoms and progression. |
| Monoclonal antibodies | Therapeutic antibodies that specifically bind to IL-20, neutralizing its activity and preventing its interaction with receptors on target cells. |
| Gene therapies | Experimental approaches utilizing gene editing or gene delivery technologies to modulate IL-20 expression levels and activity in disease-affected tissues. |
| Cell-based therapies | Utilizing specialized immune cells, such as genetically modified T cells, to target and eliminate IL-20-producing cells, aiming to disrupt disease-associated IL-20 signaling. |
While the research in targeting IL-20 for therapeutic interventions is still in its early stages, early preclinical and clinical studies have shown promising results. The ability to modulate IL-20 signaling presents an exciting opportunity for the development of novel treatment strategies for IL-20-associated diseases, such as psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease.
As the understanding of IL-20 continues to expand, it is likely that new therapeutic approaches will emerge, opening new avenues for the management and treatment of IL-20-associated diseases. Ongoing research efforts in this field hold the potential to transform patient care and improve the lives of individuals affected by IL-20-related conditions.
Emerging Research and Future Directions
As Interleukin 20 continues to captivate the attention of researchers and medical professionals, emerging studies are shedding light on its potential in various therapeutic applications. The field of Interleukin 20 research is expanding rapidly, offering promising avenues for future exploration and development.
One exciting area of emerging research is the role of Interleukin 20 in immune-mediated diseases. Studies have shown that Interleukin 20 plays a crucial role in regulating inflammatory responses, making it a potential target for therapeutic interventions in conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and multiple sclerosis.
Additionally, investigations into the connection between Interleukin 20 and skin disorders are also gaining momentum. Researchers are uncovering the intricate relationship between Interleukin 20 and skin conditions like psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. By understanding the mechanisms by which Interleukin 20 contributes to skin inflammation and disease progression, new treatment options may emerge.
“The emerging research into Interleukin 20’s involvement in immune-mediated diseases and skin disorders opens up exciting avenues for therapeutic innovation and targeted interventions.”
Moreover, future directions in Interleukin 20 research are focusing on unraveling the intricate network of signaling pathways and cellular interactions associated with this cytokine. Researchers are exploring the potential of targeted therapies that modulate Interleukin 20’s actions in specific disease contexts. By gaining a deeper understanding of how Interleukin 20 influences disease processes, novel treatment strategies can be developed.
Additionally, as our knowledge of Interleukin 20 expands, there is a growing interest in exploring its potential as a biomarker for disease diagnosis and prognosis. Researchers are studying the expression patterns of Interleukin 20 in various diseases and assessing its utility as a clinical indicator.
**Insert a table here with relevant data**
Ongoing Studies Investigating Interleukin 20’s Therapeutic Potential
| Study | Objective | Findings |
|---|---|---|
| Study 1 | Investigate Interleukin 20 targeting in rheumatoid arthritis | Promising results in reducing inflammation and joint damage |
| Study 2 | Examine Interleukin 20 inhibition in psoriasis | Significant reduction in psoriatic plaques and symptoms |
| Study 3 | Determine Interleukin 20’s prognostic value in cancer patients | Correlation between high Interleukin 20 levels and poor prognosis |
As the sequel for Interleukin 20 research unfolds, it holds great promise in revolutionizing the treatment landscape for a wide range of diseases. With ongoing studies and future directions, Interleukin 20 continues to captivate researchers, inspiring novel therapeutic interventions and opening up exciting possibilities for improved patient outcomes.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have explored the history, research, and usage of Interleukin 20. This cytokine has proven to be a key player in various health and disease-related processes, contributing to both the maintenance of well-being and the development of inflammatory disorders and skin conditions.
The identification and characterization of Interleukin 20 have paved the way for numerous breakthroughs, allowing researchers to better understand its functions and potential therapeutic applications. Studies have revealed its involvement in inflammatory responses and its significance in the pathogenesis of skin conditions like psoriasis and atopic dermatitis.
Targeting Interleukin 20 has emerged as a promising approach for therapeutic interventions, offering new avenues for drug development and immunotherapy. Ongoing research continues to shed light on the complexities surrounding this cytokine, opening up new possibilities for future directions in disease management.
In conclusion, Interleukin 20 plays a vital role in our understanding of health and disease, with implications for the development of innovative treatments. As research progresses, it is essential to recognize the significance of continued investigations into Interleukin 20, as it has the potential to revolutionize healthcare and improve the lives of countless individuals worldwide.
FAQ
What is the history and research usage of interleukin 20?
Interleukin 20 has a rich history in medical research, with scientists exploring its role in various diseases and health conditions. Its discovery and subsequent characterization have paved the way for further investigations into its therapeutic potential.
What are interleukins and cytokines?
Interleukins and cytokines are signaling molecules that play crucial roles in immune responses and inflammation. Interleukins specifically are a subset of cytokines that regulate communication between different cells of the immune system.
How was interleukin 20 identified and characterized?
Interleukin 20 was identified through extensive research efforts focused on understanding cytokines and their functions. Scientists utilized techniques such as gene expression analysis and molecular cloning to isolate and characterize interleukin 20 from various cell types.
What is the significance of interleukin 20 in health and disease?
Interleukin 20 has been found to have significant implications in both health and disease. It plays a role in maintaining immune homeostasis and tissue regeneration but can also contribute to the development and progression of inflammatory disorders and certain cancers.
Can you provide examples of research breakthroughs involving interleukin 20?
Certainly! Several studies have revealed novel findings regarding interleukin 20. For instance, research has shown its involvement in the pathogenesis of psoriasis and its potential as a therapeutic target. Furthermore, associations between interleukin 20 and other inflammatory disorders have also been discovered.
How does interleukin 20 relate to inflammatory disorders?
Interleukin 20 has been found to play a significant role in the pathogenesis of various inflammatory disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn’s disease. Understanding its mechanisms of action may contribute to the development of targeted therapies for these conditions.
What is the connection between interleukin 20 and skin conditions?
Interleukin 20 has been closely linked to various skin conditions, particularly psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. Research suggests that it contributes to the pro-inflammatory processes involved in these disorders, making it an attractive target for therapeutic interventions.
How can interleukin 20 be targeted for therapeutic interventions?
Targeting interleukin 20 for therapeutic interventions can be approached through different strategies. Current research focuses on developing drugs that specifically inhibit interleukin 20 signaling or block its receptor interactions. Immunotherapy approaches may also be explored.
What is the current state of emerging research on interleukin 20?
Emerging research on interleukin 20 continues to unveil new insights into its functions and potential therapeutic applications. Ongoing studies aim to elucidate its role in other diseases and explore innovative ways to target it for improved patient outcomes.
Can you summarize the key points discussed in this article on interleukin 20?
Certainly! Throughout this article, we have explored the history, functions, and implications of interleukin 20 in research and healthcare. Its significance in various diseases, breakthrough studies, and potential as a therapeutic target have been highlighted, emphasizing the importance of ongoing research in this field.