Blog Post
Unraveling Interleukin-30 and Beyond: Insights into Immunomodulation
Introduction Interleukin-30 (IL-30) and its related cytokines form a fascinating frontier in immunology, offering new perspectives on immune regulation and therapeutic possibilities. In this blog post, we delve into the emerging roles of IL-30 and its implications in immune modulation and disease pathways.
Understanding Interleukin-30 (IL-30) IL-30 belongs to the IL-27 cytokine family and plays a pivotal role in modulating immune responses. It acts in concert with other cytokines to fine-tune immune reactions, impacting both innate and adaptive immunity.
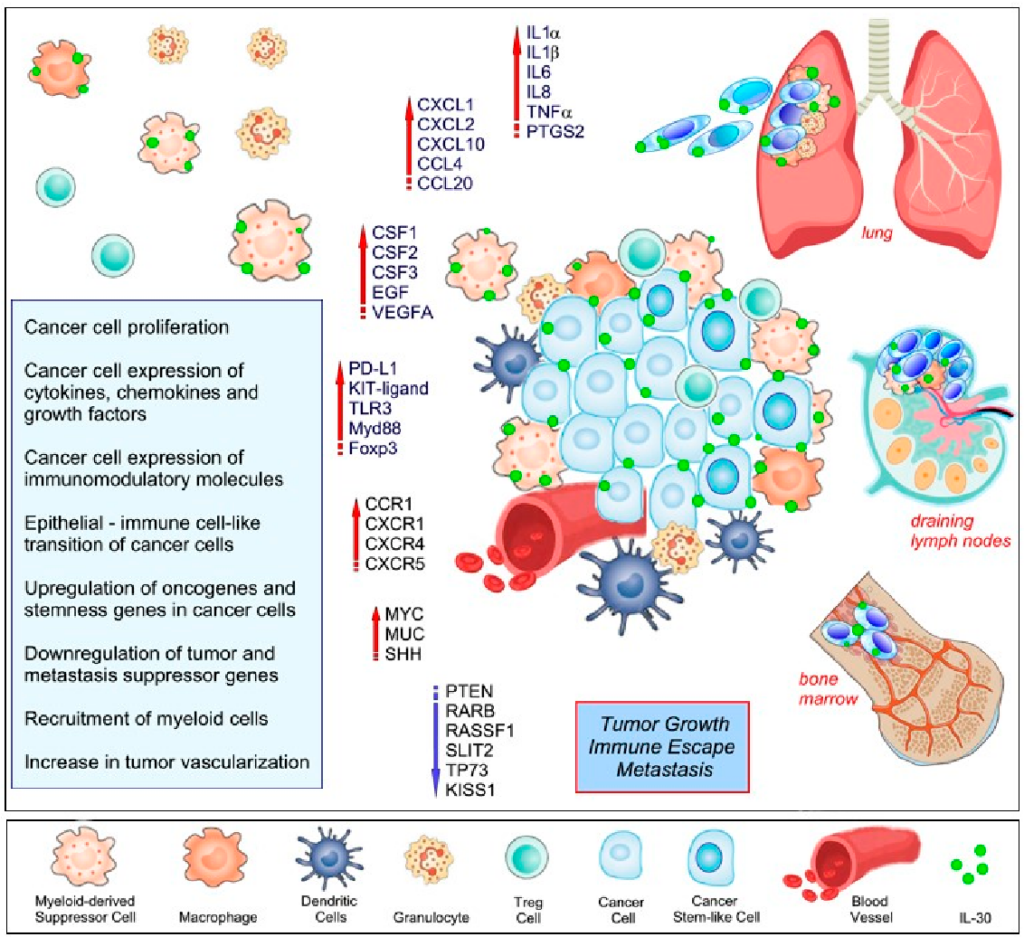
Decoding the Role of Interleukin-30 in the Crosstalk between Cancer and Myeloid Cells
Diverse Functions of IL-30
- Immunoregulation: IL-30 exerts immunoregulatory effects by influencing the activity of immune cells such as T cells, B cells, dendritic cells, and natural killer cells, contributing to immune balance and tolerance.
- Inflammatory Responses: IL-30 participates in the regulation of inflammatory processes, affecting cytokine production, immune cell recruitment, and tissue responses during inflammation.
- Antitumor Activity: Emerging evidence suggests a potential role for IL-30 in antitumor immunity, with implications for cancer immunotherapy and immune checkpoint modulation.
Significance of IL-30 in Health and Disease
- Autoimmune Disorders: Dysregulation of IL-30 signaling is implicated in autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and lupus, highlighting its role in autoimmune pathogenesis.
- Infectious Diseases: IL-30’s involvement in immune responses against pathogens underscores its relevance in infectious disease settings, including viral, bacterial, and parasitic infections.
- Cancer Immunotherapy: IL-30’s immunomodulatory properties offer potential avenues for enhancing antitumor immune responses and developing novel immunotherapeutic strategies against cancer.
Therapeutic Potential and Research Advances Researchers are exploring IL-30 as a therapeutic target for immune-related disorders and cancer, investigating strategies such as IL-30 blockade, receptor modulation, and combination therapies to harness its immunomodulatory effects.
Future Directions and Clinical Implications Ongoing studies aim to elucidate the intricate mechanisms of IL-30 signaling, its interactions with other immune mediators, and its role in specific disease contexts. Insights from research hold promise for advancing personalized medicine and developing targeted immunotherapies.
Conclusion Interleukin-30 (IL-30) emerges as a key player in immune regulation, inflammation, and potential therapeutic interventions across various disease spectrums. Unraveling the complexities of IL-30 signaling opens new avenues for precision medicine and innovative immunotherapeutic approaches.

