Blog Post
Interleukin-18 (IL-18): Decoding its Role in Immunity and Disease
Interleukin-18 (IL-18) is a pivotal cytokine that plays a crucial role in modulating immune responses and contributing to the intricate balance of the immune system. Discovered in the late 1980s, IL-18 has since been a subject of extensive research, uncovering its multifaceted functions and implications in various diseases.
1. Unveiling IL-18: A Historical Perspective
The journey of IL-18 began with its identification by researchers in the late 1980s. Initially known as interferon-gamma-inducing factor (IGIF), IL-18 was recognized for its ability to induce the production of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). Subsequent studies revealed its broader impact on immune regulation, sparking interest in its diverse functions.
2. Molecular Dynamics of IL-18
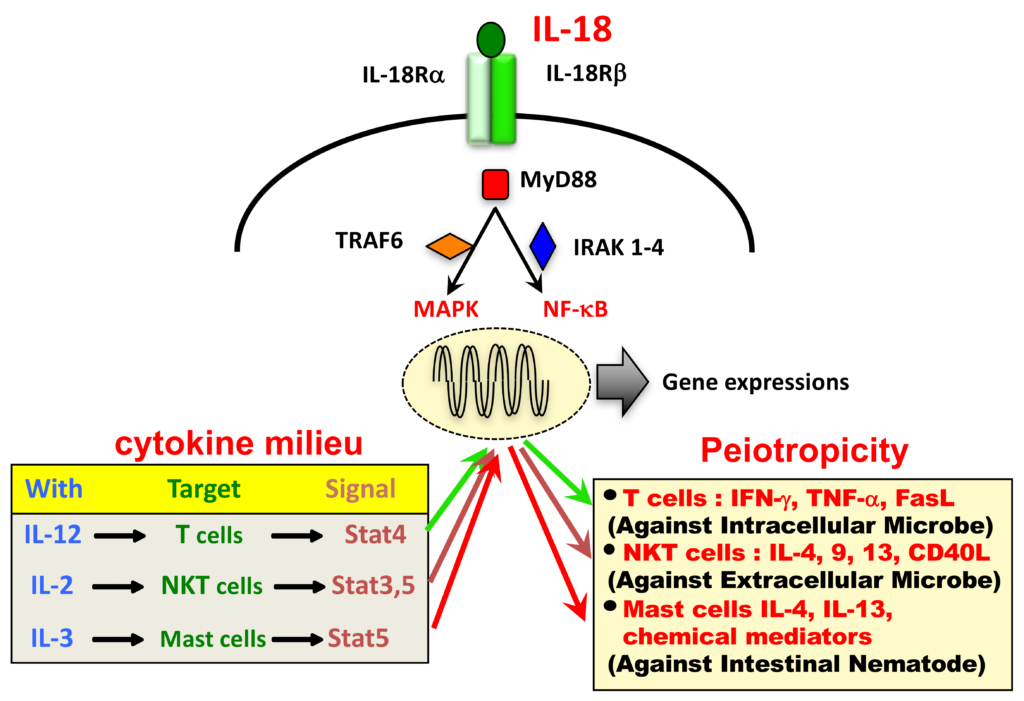
At the molecular level, IL-18 is synthesized as an inactive precursor that requires processing by specific enzymes to become biologically active. As a member of the IL-1 superfamily, it shares a signaling pathway with IL-1β, engaging the IL-18 receptor complex. This interaction triggers downstream cascades, influencing immune cell activation and cytokine production.
3. Immunomodulatory Functions of IL-18
IL-18 acts as a pleiotropic cytokine, exerting both pro- and anti-inflammatory effects depending on the context of the immune response. It plays a crucial role in enhancing the production of IFN-γ and other pro-inflammatory cytokines, contributing to host defense against infections. Simultaneously, IL-18 is involved in regulatory processes that maintain immune homeostasis.
4. IL-18 in Infectious Diseases
The cytokine’s involvement in infectious diseases highlights its significance in host defense mechanisms. IL-18 contributes to the activation of natural killer (NK) cells and T cells, promoting effective immune responses against pathogens. Understanding these interactions provides valuable insights into potential therapeutic strategies for infectious diseases.
5. IL-18 and Autoinflammatory Disorders
Aberrant IL-18 regulation has been implicated in various autoinflammatory disorders, where dysregulated cytokine production contributes to chronic inflammation. Conditions such as hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) underscore the delicate balance required for IL-18-mediated immune responses.
6. Therapeutic Implications and Future Directions
The intricate involvement of IL-18 in immune regulation positions it as a potential therapeutic target. Modulating IL-18 activity holds promise for interventions in inflammatory and autoimmune conditions. However, the complexity of its functions requires comprehensive exploration for targeted therapeutic development.
In conclusion, Interleukin-18 emerges as a key orchestrator in the immune symphony, influencing responses against infections and contributing to immune homeostasis. From its historical discovery to ongoing investigations into therapeutic applications, IL-18 continues to captivate researchers, offering avenues for deeper insights into immune-mediated diseases.