Blog Post
Decoding the Chronicles: Tracing the Journey of Interferon-1 (IFN-I) in Immunology
Embark on a captivating journey through the annals of immunological history as we unravel the story of Interferon-1 (IFN-I). From its discovery as a pivotal component of the immune system to its multifaceted roles in antiviral defense and immune modulation, this exploration sheds light on the remarkable contributions of IFN-I to our understanding of host defense mechanisms.
1. Dawn of Discovery: IFN-I Emerges on the Immunological Horizon
Our odyssey commences with the discovery of IFN-I, a groundbreaking revelation that emerged from investigations into the body’s response to viral infections. In the mid-20th century, researchers exploring the mechanisms of viral interference stumbled upon a mysterious substance capable of conferring resistance to viral infections. This substance, later identified as IFN-I, marked a paradigm shift in our understanding of how the immune system recognizes and combats viral threats. Its diverse subtypes, including IFN-α and IFN-β, showcased a spectrum of functions, underscoring the complexity of the host’s antiviral defense arsenal.
2. Guardians of Antiviral Defense: IFN-I’s Role in Immune Surveillance
As we navigate deeper into IFN-I’s narrative, its role as a guardian of antiviral defense takes center stage. IFN-I serves as a sentinel, activating an array of cellular responses that collectively fortify the host’s defenses against viral replication and spread. The induction of an antiviral state in neighboring cells represents just one facet of IFN-I’s multifaceted arsenal. Beyond directly impeding viral replication, IFN-I orchestrates a symphony of immune responses, influencing the activation and function of various immune cells. This orchestration positions IFN-I as a key player in the complex interplay between the immune system and infectious agents.
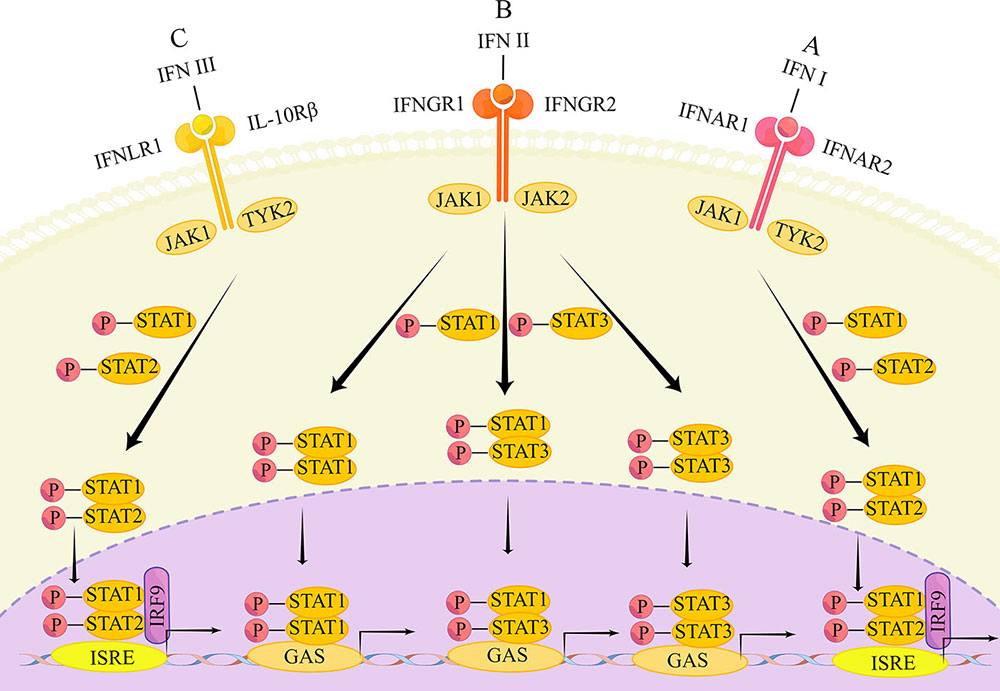
3. Unraveling Signaling Pathways: Insights into IFN-I’s Molecular Dance
Delve into the molecular intricacies of IFN-I signaling pathways, where a complex dance of molecular interactions determines the outcomes of antiviral defense and immune modulation. IFN-I engages with specific cell surface receptors, triggering a cascade of events that culminate in the activation of genes responsible for antiviral defense. The Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription (JAK-STAT) pathway stands out as a key player in this intricate molecular ballet, providing a glimpse into the precision and specificity of IFN-I responses.
Stay tuned for subsequent chapters, where we unravel the broader roles of IFN-I in immune modulation and its potential therapeutic applications.